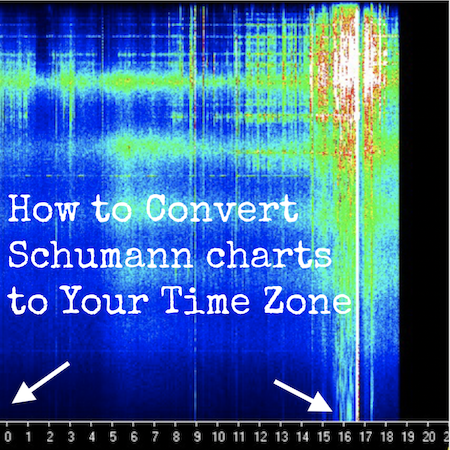
 Learn how to convert your time zone to the Schumann Resonance charts by Space Observing System, from any time zone in the world.
Learn how to convert your time zone to the Schumann Resonance charts by Space Observing System, from any time zone in the world.
These instructions are for the Schumann Resonance Charts put out by Space Observing System in Tomsk, Russia, which is in the GMAT/UT +7 hours time zone.
I’ve created easy to share images, followed by USA time zone conversion charts, and then a written discussion, below.
If you have questions, please message me at my contact page. I’m also taking requests there for converting the charts to your specific time zone.
Contact page: https://bit.ly/2xrUOPS
Bitly link to this article for easy sharing: https://bit.ly/2CevuQ5
A French translation of this text is in the last section of this article.
How to Convert Schumann Resonance Data Chart Time – Anywhere in the World
Shareable images in Parts 1, 2, and 3 – written discussion of this same material appears below.



USA Conversion Charts:
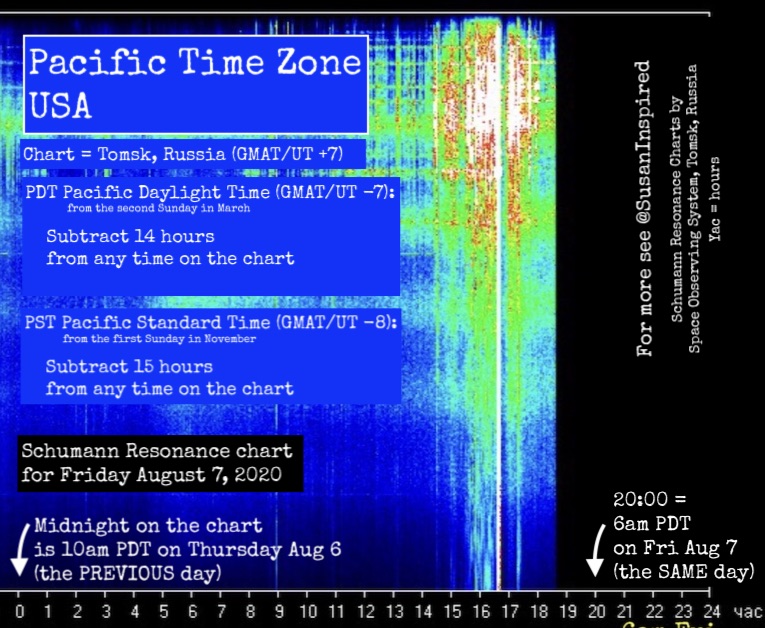
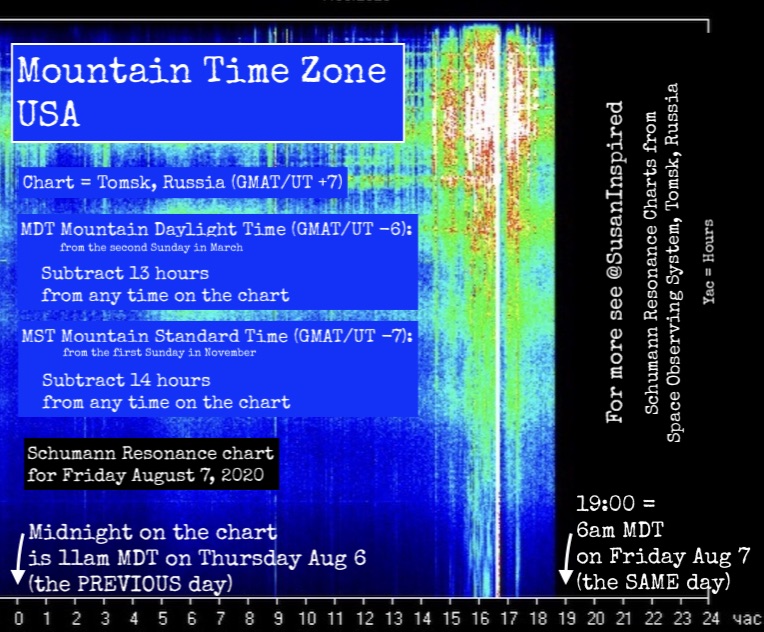

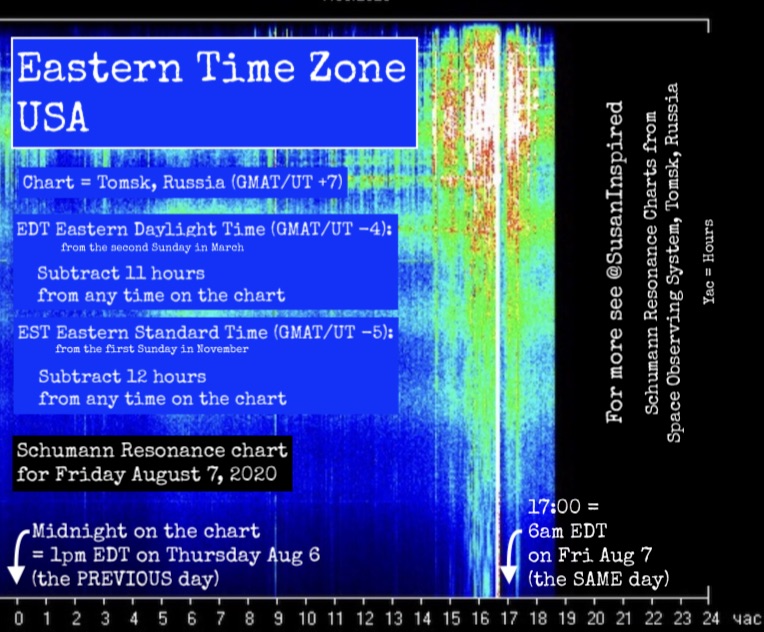
How to Convert Schumann Resonance Data Chart Time to the Time at Your Location
This is a detailed discussion of how to do time conversions for these charts and they will work from anywhere in the world.
All you need to know is what your time is relative to GMAT/UT time, which is considered time zone ‘zero’ for all time calculations. Your time zone will be ‘plus’ or ‘minus’ GMAT/UT time. For example, San Francisco is GMAT/UT -7 hours. Tokyo is GMAT/UT +9 hours.
If you live near Greenwich, England, you are on GMAT/UT time zero and can convert the chart by adding seven hours to it, since Tomsk, Russia is seven hours ahead of GMAT time (GMAT/UT +7 hours).
The rest of us can follow this process to do the time conversion (this is the same information as in the image above):
1. Find out what your Universal Time (UT) time zone is – also known as your GMAT time zone (GMAT).
The UT – GMAT time zone equates with ‘time zone zero’, and it initiates at the longitude of the Earth for Greenwich, England.
How to find out your UT – GMAT time zone:
Put your city and country into Google like this:
San Francisco USA Universal Time, or
San Francisco USA Time Zone
The Schumann Resonance Charts by Space Observing System are on the time zone for Tomsk, Russia, which is UT +7 hours (GMAT +7 hours).
2. Convert from Your Time Zone to the Tomsk Time Zone, Here’s How:
Your timezone is either MINUS GMAT (subtract hours from GMAT) or PLUS GMAT (add hours to GMAT).
For ‘MINUS’ GMAT time zones:
Add your time zone difference from GMAT with the time zone difference from UT/GMAT for Tomsk (which is 7), to get your time difference from the charts.
If your time zone difference from GMAT is 3 hours, for example you are in time zone GMAT -3, then add the two time zone differences to get your time difference from the charts.
So in this example that would be 7 (Tomsk) plus 3 (example time zone) equals 10 hours time difference from Tomsk. 3+7 = 10 hours time difference from Tomsk, Russia.
THEN SUBTRACT 10 hours from the hour on the chart to convert to your time zone.
For this example converting time zone GMAT -3 to Tomsk time, subtract 10 hours from the hours on the flat axis (the X axis) of the chart.
So for our example using the GMAT -3 time zone, if you are looking at 12 noon on the Schumann Resonance chart, then subtract 10 hours to get your time: 12 – 10 = 2 or, noon minus 10 hours equals 2am the same day.
If you had a 14 hours difference from Tomsk, i.e., you are in GMAT -7 (like the west coast of the USA), then noon on the Schumann chart is 10pm the PREVIOUS DAY.
For ‘PLUS’ GMAT time zones:
If your time zone is PLUS GMAT/UT, then, how you calculate the time conversion depends if you are east or west of Tomsk, Russia.
East of Tomsk would be your UTC time zone plus less-than-seven-hours.
West of Tomsk would be your UTC time zone plus more-than-seven-hours.
EAST OF TOMSK (i.e., most of Europe, Africa, Middle East, some Russia):
If your time zone is GMAT/UT plus less-than-seven-hours, for example, if your are at GMAT +2, you calculate 7-2 to get a 5 hour time difference.
Then SUBTRACT 5 hours from the time on the charts to convert the hours to your time zone.
So for example if your time zone is GMAT +2, then 12 noon in Tomsk is 7am your time.
WEST OF TOMSK (i.e., much of Russia, China, Japan, Australia)
If your time zone is GMAT +8, you SUBTRACT 8-7 to get a 1 hour time difference from the charts.
Then ADD the remainder (in this example, that’s 1 hour) to the time on the charts to convert the hours to your time zone.
So for GMAT +8, then 12 noon in Tomsk is 1pm your time.
By Request – French Translation
1. Découvrez quel est votre fuseau horaire de temps universel (UT) – également appelé votre fuseau horaire GMAT (GMAT).
Le fuseau horaire UT – GMAT équivaut au «fuseau horaire zéro», et il commence à la longitude de la Terre pour Greenwich, en Angleterre.
Comment connaître votre fuseau horaire UT – GMAT:
Mettez votre ville et votre pays dans Google comme ceci:
Temps universel de San Francisco, États-Unis, ou
Fuseau horaire de San Francisco États-Unis
Les cartes de résonance Schumann par système d’observation spatiale sont sur le fuseau horaire de Tomsk, en Russie, qui est UT +7 heures (GMAT +7 heures).
2. Passez de votre fuseau horaire au fuseau horaire de Tomsk, voici comment:
Votre fuseau horaire est MINUS GMAT (soustrayez les heures de GMAT) ou PLUS GMAT (ajoutez les heures au GMAT).
Pour les fuseaux horaires GMAT «MOINS»:
Ajoutez votre décalage horaire par rapport à GMAT avec le décalage horaire de UT / GMAT pour Tomsk (qui est 7), pour obtenir votre décalage horaire à partir des graphiques.
Si votre différence de fuseau horaire par rapport à GMAT est de 3 heures, par exemple si vous êtes dans le fuseau horaire GMAT -3, ajoutez les deux différences de fuseau horaire pour obtenir votre décalage horaire à partir des graphiques.
Donc, dans cet exemple, ce serait 7 (Tomsk) plus 3 (exemple de fuseau horaire) équivaut à 10 heures de décalage horaire par rapport à Tomsk. 3 + 7 = 10 heures de décalage horaire par rapport à Tomsk, Russie.
PUIS SOYEZ 10 heures de l’heure sur le graphique pour convertir votre fuseau horaire.
Pour cet exemple de conversion du fuseau horaire GMAT -3 en heure de Tomsk, soustrayez 10 heures des heures sur l’axe plat (l’axe X) du graphique.
Donc, pour notre exemple utilisant le fuseau horaire GMAT -3, si vous regardez 12h00 sur le graphique de résonance Schumann, soustrayez 10 heures pour obtenir votre temps: 12-10 = 2 ou, midi moins 10 heures équivaut à 2 heures du matin le même jour .
Si vous aviez une différence de 14 heures par rapport à Tomsk, c’est-à-dire que vous êtes en GMAT -7 (comme la côte ouest des États-Unis), alors midi sur la carte Schumann est 22 heures le JOUR PRÉCÉDENT.
Pour les fuseaux horaires GMAT «PLUS»:
Si votre fuseau horaire est PLUS GMAT / UT, la façon dont vous calculez la conversion de temps dépend si vous vous trouvez à l’est ou à l’ouest de Tomsk, Russie.
À l’est de Tomsk serait votre fuseau horaire UTC plus moins de sept heures.
À l’ouest de Tomsk serait votre fuseau horaire UTC plus plus de sept heures.
À L’EST DE TOMSK (c’est-à-dire la plupart de l’Europe, l’Afrique, le Moyen-Orient, une partie de la Russie):
Si votre fuseau horaire est GMAT / UT plus moins de sept heures, par exemple, si vous êtes à GMAT +2, vous calculez 7-2 pour obtenir un décalage horaire de 5 heures.
SOYEZ ensuite 5 heures de l’heure sur les graphiques pour convertir les heures en votre fuseau horaire.
Ainsi, par exemple, si votre fuseau horaire est GMAT +2, alors midi à Tomsk est 7 heures du matin.
À L’OUEST DE TOMSK (c’est-à-dire une grande partie de la Russie, de la Chine, du Japon, de l’Australie)
Si votre fuseau horaire est GMAT +8, vous SOYEZ 8-7 pour obtenir un décalage horaire d’une heure par rapport aux graphiques.
AJOUTEZ ensuite le reste (dans cet exemple, 1 heure) à l’heure des graphiques pour convertir les heures en votre fuseau horaire.
Donc pour GMAT +8, alors midi à Tomsk c’est 13h votre heure.
Cette traduction a été réalisée avec Google Translate. Pour corriger cette traduction, veuillez m’envoyer un message ici: https://bit.ly/2xrUOPS
If you liked it, please share this article on social media, forums or email, this really helps me.
*
Please Join my Mailing List and Get Inspired!
Joy, Inspiration, Soul Connection, and Fulfillment can be yours!
1) Get a monthly update listing all my content in one place;
2) Stay in touch independent of social media practices and policies;
3) Receive news on upcoming courses and new content; and
4) Get my monthly summary of the energies and events this month.
© 2020 Susan Lacerra. All Rights Reserved. Permission is given to share this article on other blogs and websites as long as the text is posted, in part or in whole, without alteration and with the author’s credit and live website link included in the article. This article was first published on August 9, 2020 – easy to share link is https://bit.ly/2CevuQ5. Thank you for sharing!